General shipboard testing
After the Factury Acceptance Tests are completed to satisfaction, the equipment has to be installed on board. When completed, a new series of tests has to be carried out: The Harbour Acceptance Test, or HAT.
Before this testing can be carried out, cables, pipes, safety systems, such as firedetection, bilgealarm, etc, have to be ready and have to be tested. This is in fact pre-testing, and part of the HAT. There is an overlap with the actual HAT, which is carried out when all systems and equipment is supposed to be ready.Before a new installation is put into service, the following tests are to be carried out. These tests are in addition to any acceptance tests which may have been carried out at the manufacturer's .
1. Insulation resistance
The insulation resistance of all systems and electrical equipment has to be measured using a direct current insulation tester, between: a. connected current carrying parts b. as far as reasonably practicable all current carrying parts of different polarity or phase.
The installation may be subdivided and equipment may be disconnected if initial tests produce resistance values lower than the required resistances.
2. Earth conductors
Tests are to be carried out to verify the effectiveness of the earth continuity conductor and the earthing of non-current carrying exposed metal parts of electrical equipment and cables.
3. Generators
Tests are required to demonstrate satisfactory performance of each generator and engine by means of a test run at full rated load and at 110% overload for at least 15 minutes. Engine temperatures should stabilize and not exceed the maximum figures as determined by the manufacturer.
Example of part of Megger list
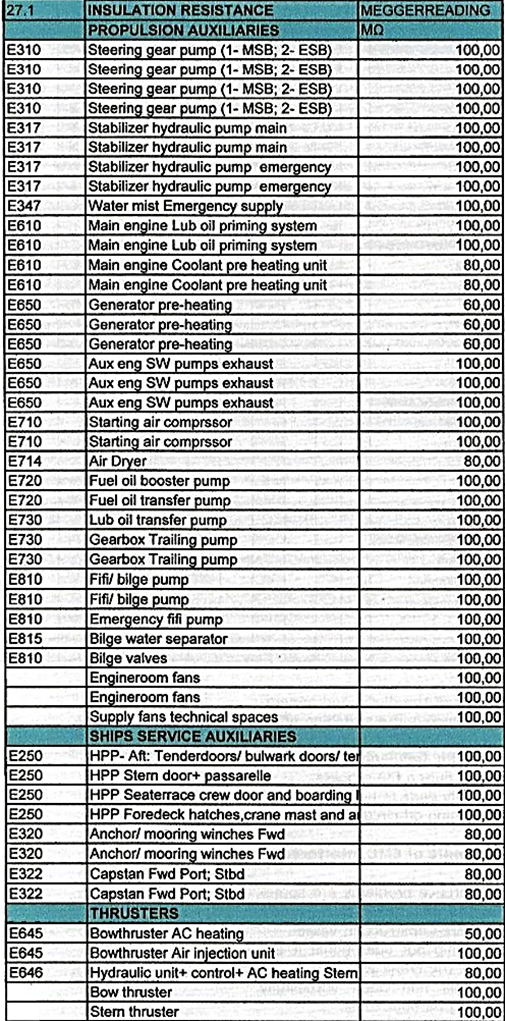
Minimum test voltage and insulation resistance M_a

4. Switchboards
During the full load tests, the temperatures of joints, connections, circuit breakers, bus-bars and fuses have to be monitored and may not exceed the maximum values. For cables with XLPE insulation this value should be below 85°C. Bus-bars in switchboards may reach 95 °C.
5. Synchronising equipment
During functional tests the operation of engine governors, synchronizing devices, overspeed trips, reversecurrent relays, reverse-power and over-current trips and other safety devices must be demonstrated. Generators with a rating of more than 1500kVA must also be protected by a differential protection system, showing a possible current leakage.
6. Automatic Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator of each generator has to be tested by opening its breaker when the generator is running at full load and also when starting the largest motor which is connected to the system.
Also the speed governor has to be tested by opening the circuit breaker at full load. This is not to result in overspeed trip. The minimum speed of a diesel generator has to be verified when starting the largest electric motor on board.
7. Parallel operation
Parallel operation and kW and kVA load sharing of all generators capable of being operated in parallel mode, at all loads up to normal working load, has to be tested.
8. Functional test
Essential equipment must be operated under service conditions, though not necessarily at full load or simultaneously, for a sufficient length of time to demonstrate that the temperatures stabilize and equipment does not overheat.
9. Safety systems
Fire, crew and passenger and ship safety systems must be tested for correct functioning.
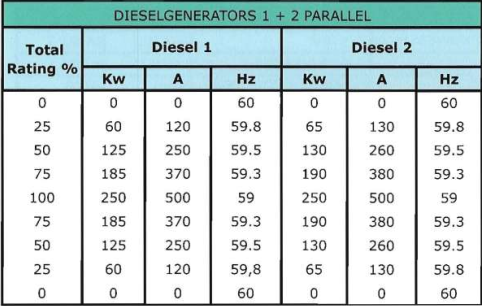
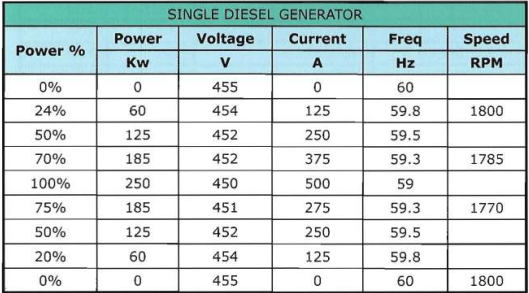
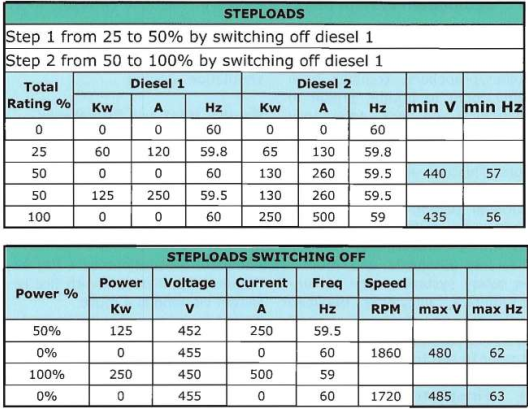
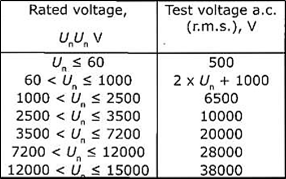
High Voltage test voltage depends on the nominal voltage of the system as in the following table:
10. General alarm systems
On completion of the general emergency alarm system and the public address system tests, the surveyor has to be provided with two copies of the test schedule, detailing the measured sound pressure levels. Such schedules are to be signed by the surveyor and the builder.
 +7 (812) 4-673-673
+7 (812) 4-673-673