General principles of the GMDSS
General principles of the GMDSS
Global Maritime Safety and Maritime Safety (GMDSS) was developed by the maritime nations within the framework of the International Maritime Organization (IMO). It is the result of the adoption of amendments in 1988. to the International Convention for the Protection of Life at Sea (SOLAS) of 1974.
The GMDSS is designed to provide maximum accessibility of communications related to the safety of all ships, passenger and cargo, with a gross tonnage of 3,000 tons that are on international flights. For vessels with a tonnage of less than 300 reg., As well as those not involved in international flights, the requirements of the administration of their national flag apply.
To ensure maximum safety of navigation, the latest developments in the field of maritime communications, such as satellite systems and digital technologies, are used. The GMDSS guarantees the provision of appropriate vessels with communication with coastal services in case of emergency situations and for the exchange of safety information, around the clock and at any location.
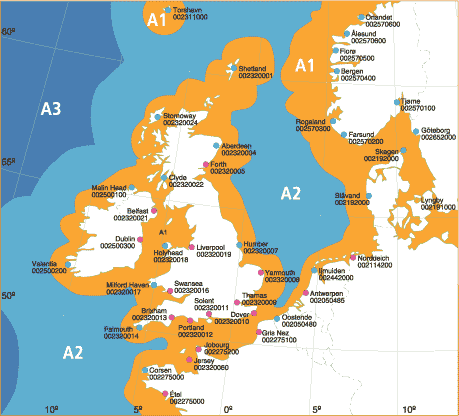
Marine areas
The GMDSS divides the world's oceans into 4 marine regions based on the location and communication capabilities of coastal stations: A1, A2, A3 and A4. The figure shows an example of European marine areas.
Main advantages of the GMDSS
1. GMDSS ships are equipped with communication equipment intended for the sea area of their navigation, and are able to use long-distance communication if necessary. This means that the distress signal will be heard by the coast station and other vessels. (Previously, due to the limited range of distress calls and 500 and 2182 kHz calls used for these purposes, there was the possibility of unrecognized calls if ships and coast stations were out of reach of signals.) The GMDSS solved this problem.2. Since GMDSS vessels have been equipped with standardized equipment for a specific sea area and use the same frequencies, compatibility is ensured between search and rescue services and ships.
3. The GMDSS equipment allows you to give a distress call by pressing a special button located on the ship's ground MF / HF, VHF or Inmarsat station with DSC. If this is not possible to make a distress call, a freely pop-up emergency emergency beacon emanates. (The success of the distress signal is no longer dependent on the qualifications of the ship's radio operators)
Requirements for equipping ships with GMDSS equipment
 +7 (812) 4-673-673
+7 (812) 4-673-673