Communication systems
Communication systems
1. GMDSS
1.1. GMDSS equipment
Names and functions of compulsory GMDSS equipment is as follows. All ships, all areas:
1. EPIRB stands for an Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon. It is capable of automatically giving the position of a ship when the ship is submerged and the EPIRB has floated up; the code also includes the identification of the ship.
2. SART is a Search And Rescue Radar Transponder relaying the identification of the ship when hit by the radar beam of a 10 cm radar.
3. NAVTEX receives meteorological, navigational and safety information, in relation to maritime safety.
4. DSC or Digital Selective Calling. This is a means of alerting in the case of distress without the
use of satellites. The operational area is limited by the availability of shore based maritime rescue co-ordination centers.
Communication equipment area Al:
5. One self-contained EPIRB satellite radio beacon
6. One fixed VHF Radio telephone with whip aerials
7. One self-contained SART radar transponder
8. One NAVTEX receiver with whip aerial
9. One enhanced group radio with whip antenna
10. Two hand-held autonomous VHF radiotelephones
Area A2 includes the above plus the following:
11.One MF Radiotelephone with Digital Selective Calling and either a wire aerial or a tall vertical whip aerial between 9 and 16 metres high or alternatively.
12.One INMARSAT-C satellite communication system with a gyro stabilized, omnidirectional antenna teletype and data. New miniature system SATCOM-M has voice fax and data capabilities and a gyro stabilised directional antenna.
For A2 MF/HF with DSC is mandatory. VHF must be duplicated. Sat- com is not Mandatory. Most in use is SATCOM-C. Newest used Satcom is Inmarsat-F and Fleet Broadband.
A3 includes the above plus the following:
13. One MF Radio telephone system and an INMARSAT-C system with aerials or alternatively, as duplication for the Satcom systems, another MF/HF radio telephone system with DSC and TELEX with another large wire aerial or tall whip.
MF/HF and Satcom C. Telex on MF/ HF is required or a 2nd Satcom C Three hand-held VHF self-contained radio telephones.
Area A4 is beyond the coverage of the satellites, only the duplicated MF/HF Radiotelephone systems with DSC and TELEX are acceptable.
1.2. AIS, LRIT and SSAS
1.2.1. Automatic Identification System
AIS is a transponder system that transmits the ship's data: name, call sign, dimensions, type of ship, IMO number and variable data as position, course and speed, draught, cargo, destination and Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) in the VHF band.
The data received from the vessel are processed and combined with the next map of the area where the ship sails and nowadays also posted on the internet. The picture on the next page shows an example of the ships sailing in the English channel with details of one vessel in a pop-up screen after "mouse over".


ARB
1.2.2. Long Range Identification and Tracking system (LRIT)
The ISPS regulations of IMO require ships to transmit their position every six hours to a central database. This allows flagstates to verify the position of vessels in their administration worldwide. This data is transmitted automatically through a suitable transmission system in the radio zones for which the vessel is certified.
The LRIT equipment has to be type- approved.
1.2.3. Ship Security Alert System
A Ship Security Alert System (SSAS) is a satellite radio system, providing the ship's staff with a means to alert the homebase, in case of for instance a pirate attack. In the wheelhouse and somewhere else in the ship, usually the engine room control room, an alarm pushbutton is installed. When this pushbutton is used an automatically arranged radio alarm message will be sent to an appointed agent, who on reception can warn the operator and authorities.
1.2.4. Antennas
All equipment mentioned above requires aerials of some sort which have to be located on the topside of the ship. Each aerial has its preferred location, but as space is limited, a compromise has to be found based on the purpose of the ship. Possible interference between the antennas must also be considered (see chapter on EMC).
Other equipment that requires aerials are radio and tv systems and for instance a V-Sat system for telephone and internet communications. More often these are gyro stabilized dish antennas, mounted in domes, that use satellites for data transfer.
2. Maintenance
Maintenance is also part of the GMDSS requirements and is defined as onboard maintenance, shorebased maintenance and maintenance by duplication of equipment on board. For ships sailing in areas Al or A2, any of these methods may be adopted in accordance with guidelines contained in the respective IMO resolution. Shore-based maintenance is the most widely adopted for all areas with the addition of duplication of equipment for areas A3 and A4.
The flag country is usually responsible for the approval of the external communication package.
3. Internal communication
A ship will also have a number of internal communication systems such as:
- public address
- general alarm
- radio paging.
Sometimes public address and general alarm are combined into one system, escpecially on passenger ships. Furthermore there may be a number of entertainment systems such as: - Radio - Satellite - Internet.
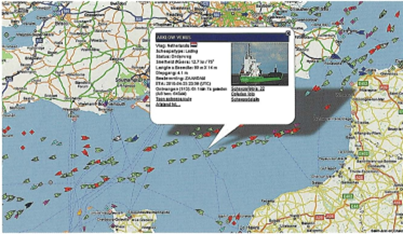
Example of AIS data. Ships in passage in the English Channel with one ship highlighted

Antenna and radar mast. Six whip aerials on left and right, two dome antennas and two radar scanners in the middle and four GPS antennas on top
 +7 (812) 4-673-673
+7 (812) 4-673-673