JRC JLR-7700MKII (DGPS)
DGPS navigator JRC The JLR-7700MKII is a navigation receiver receiving information from satellites and issuing accurate coordinates of the ship's position on the basis of this data.
The receiver can store in-memory detailed navigation information about 499 waypoints, as well as up to 100 event markers, which, if necessary, assigns eight-digit names. The device is equipped with built-in alarm, which will alert the user with a sound signal about arrival to the specified waypoint, drift, crossing the border or deviating from the paved course.
The receiver JLR-7700MKII provides several options for correction of coordinates: manual or by the standards of 46 available geodetic systems. The accuracy of determining the coordinates is: for the GPS system - 15 meters, for the DGPS - 5 meters.
The navigator is equipped with two RS-422 ports for connection to other devices and sensors. For the power supply of the device, an on-board network with a voltage of at least 10 volts is used.
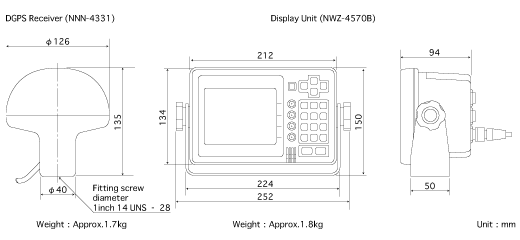
Specifications:
- GPS positioning accuracy: 15 m 2D RMS (HDOP≤4)
- Accuracy of DGPS coordinates determination: 5 m 2D RMS (HDOP≤4)
- Receiving frequency from 283.5 kHz to 325 kHz
- Frequency step: 500 Hz
- Beacon selection: Automatic or manual tuning of frequency and baud rate.
- Transmission speed: 50/100/200 bit / s
- Display Type 5-inch STN LCD, 160 x 128 pixels
- Waypoint memory Up to 499 waypoints, including 100 event tags (WPT No. 400 to 499), each point with a place name in 8 alphanumeric characters
- Operating temperature DGPS Receiver: -25 to + 55C
- Display: -15 to + 55C
- Power requirements 12/24 VDC, 10 W or less 100/220 VAC with AC power supply (option)
 12.09.2021
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis)
12.09.2021
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis)
DP notations - DP (AA) and DP (AAA) - must be verified by FMEA. This method is used to determine the consequences of a single malfunction in the motor system and its control system.
 +7 (812) 4-673-673
+7 (812) 4-673-673